

However, due to the high reactivity of potassium and sodium, the first experiment of the English chemist left no significant results. To that end, Davy attempted electrolysis on both compounds. In 1806, the English chemist Sir Humphry Davy attempted to distinguish these two substances by isolating the compounding elements. The two substances differed only based on the source they were obtained from. They called it soda ash ( sodium carbonate, Na 2 CO 3 ). At the time, people were also familiar with another similar substance that they obtained from a specific type of rock with mineral alkali properties. This is a potassium compound called potassium carbonate (K 2 CO 3 ), which was used as a cleaning agent. Since 500 A.D., people would collect the ashes from burnt wood and wash them in order to obtain potash, also referred to as vegetable alkali. In contact with air, the elemental potassium oxidizes and tarnishes very quickly. However, when it comes into contact with H 2 O (water) molecules, this soft metal reacts violently by releasing hydrogen and emitting a purple flame. This alkali element of the periodic table has an electronegativity of 0.8 according to Pauling, whereas the atomic radius according to van der Waals is 0.235 nm.Īs it has a lower density than water, potassium can actually float on it.

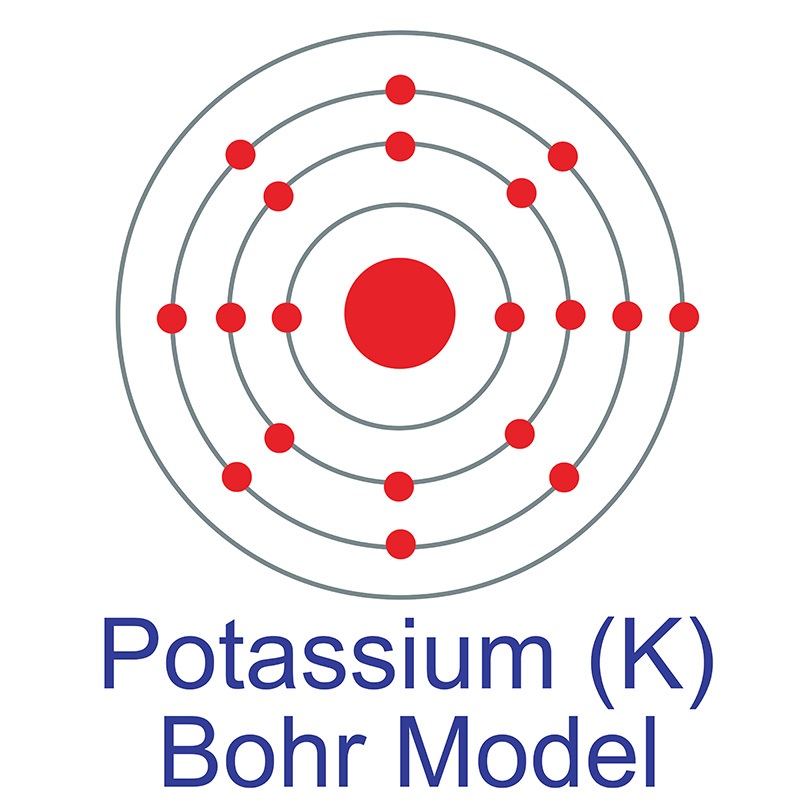
Potassium is a soft, silvery-white metal that reaches its boiling point at 759☌ (1398☏ or 1032 K), while the melting point is achieved at 63.5☌ (146.3☏ or 336.7 K). Represented by the symbol K, the chemical element potassium has the atomic number 19, an atomic mass of 39.0983 g.mol -1, and electron configuration 4s 1. The energy of the first ionization: 418.6 kj.mol -1ĭiscovery date: In 1987 by Sir Humphry Davy Half-life: From less than 10 picoseconds to 1.248×109 yearsĮlectronegativity according to Pauling: 0.8 Physical state: A soft metal at room temperature The symbol in the periodic table of elements: K Fact Box Chemical and Physical Properties of Potassium Most notably, it’s responsible for the control and regulation of the exchange of electrical impulses in the heart’s cells and within other muscles, as well as the regulation of the fluid balance within the body.

This extremely reactive chemical is also one of the most essential trace minerals found in the human body, and it’s responsible for some vital processes. As a member of the alkali metals family in the periodic table, potassium has one valence electron in its outermost shell. With about 2.0 to 2.5 percent occurrence in the Earth’s crust, it’s the eighth most abundant element found in the layers of our planet. The covalent radius of Cl 2 is half the distance between the two chlorine atoms in a single molecule of Cl 2.Potassium is a chemical element with the atomic number 19 in the periodic table of elements. (d) This is a depiction of covalent versus van der Waals radii of chlorine. (c) The van der Waals atomic radius, r vdW, is half the distance between the nuclei of two like atoms, such as argon, that are closely packed but not bonded. (b) The metallic atomic radius, r met, is half the distance between the nuclei of two adjacent atoms in a pure solid metal, such as aluminum. (a) The covalent atomic radius, r cov, is half the distance between the nuclei of two like atoms joined by a covalent bond in the same molecule, such as Cl 2.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
